OctoMap 八叉树地图库
- OctoMap
- 基本概念
- 八叉树的更新
- 0. 库的编译与安装
- 1. Data Structures
- 1.0 类间基本关系
- 1.1 Tree类
- 1.2 Node类
- 1.3 OcTreeKey
- 1.4 OctoTreeParam
- 1.5 iterator
- 1.6 ScanGraph
- 1.7 ScanNode
- 1.8 ScanEdge
- 1.9 文件格式
- Examples and Tests
- Contact
- License
Created 2022.07.11 by Cong Yu; Last modified: 2022.08.19-V2.5.7 -> 2022.08.29-V2.9.0
Contact: windmillyucong@163.com
Copyleft! 2022 Cong Yu. Some rights reserved.
OctoMap
- code https://octomap.github.io/
- API doc http://octomap.github.io/octomap/doc/
- paper http://www.arminhornung.de/Research/pub/hornung13auro.pdf
- post https://www.cnblogs.com/gaoxiang12/p/5041142.html
基本概念
- 八叉树结构
- 叶子节点的分辨率
- 每个node都有一个数据描述是否被占据
- 最简单的情况下,0空,1占据,但是没有意义
- 通常使用0-1之间的浮点数表示被占据的概率
- 好处
- 当某个节点的子节点都”占据”或者”不占据”时,且概率都相等时,可以剪枝
- 非常节省存储空间
- 实测 8M的pcd 转化为 0.01分辨率的octmap只有100多k
- 一个node本身表征了一定的占据空间,非常适合于做碰撞检测
- 树结构可以完成非常快速的检索与搜寻
- 对比pcd,可以描述运动信息(擦除机制)
- 缺点
- 信息损失
- 树结构需要维护
八叉树的更新
- 概率更新:
- reference
- 只是简单的二值贝叶斯滤波过程
-
父节点的概率,可以由子节点的概率进行计算
- 计算方式:简单的方法有:直接取平均值或者最大值。
0. 库的编译与安装
1
sudo apt-get install libqglviewer-dev-qt5
octovis
1
sudo apt-get install octovis
也可以自己编译安装octovis, 源码 https://github.com/OctoMap/octomap/tree/devel/octovis
octomap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
git clone https://github.com/Octomap/octomap.git
cd octomap
git checkout v1.9.0
mkdir build
cd build
camke ..
make -j4
sudo make install
1. Data Structures
细节详见 https://raw.githubusercontent.com/YuYuCong/BlogImg/develop/post_octmap/OcTree.drawio.png
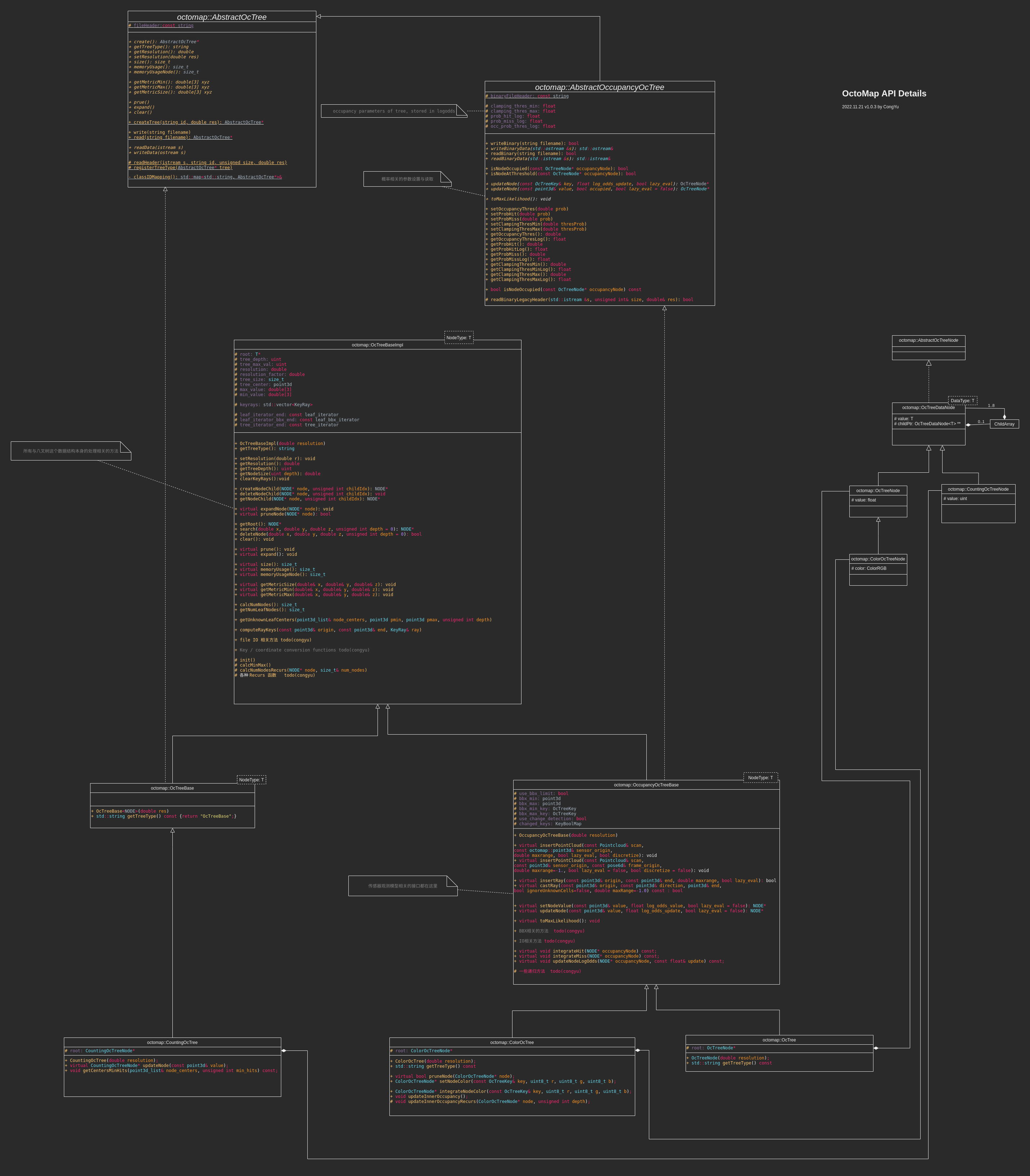
1.0 类间基本关系
注:UML类图
- 简单理解分为两类:
- tree结构类
- tree里面的数据结构类
- AbstractOctree: 万物起始。在这个类中定义了一些八叉树应该有的纯虚方法,包括但不限于:
- 设置与读取八叉树分辨率
- 获取八叉树的type string
- prune/expand/clear 等等方法
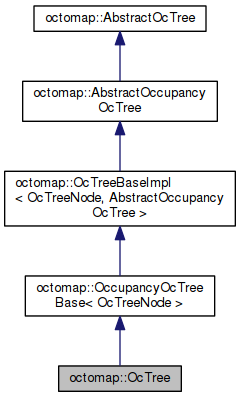
- OcTreeBase: 这个类在继承了AbstractOcTree的基础上,完整实现了octree的数据结构,包括八叉树的search\光线投射\更新node等等。
- OccupancyOcTreeBase: 在继承了OcTreeBase的基础上,引入了logOdds来表示node的占据概率。新增了insertPointcloud方法来一次性插入点云。
- OcTree/ColorOcTree:继承OccupancyOcTreeBase,是OcTree的具体实现,基本上没有新加什么东西,ColorOcTree给Node增加了颜色方法。
1.1 Tree类
1.1.1 AbstractOcTree
- file
- octomap/octomap/include/octomap/AbstractOcTree.h
- octomap/octomap/src/AbstractOcTree.cpp
方法
-
纯虚方法
-
读取八叉树分辨率
-
获取八叉树的type string
-
prune/expand/clear 等等方法
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
AbstractOcTree();
virtual ~AbstractOcTree() {};
/// returns actual class name as string for identification
virtual std::string getTreeType() const = 0;
virtual double getResolution() const = 0;
virtual void setResolution(double res) = 0;
virtual size_t size() const = 0;
virtual size_t memoryUsage() const = 0;
virtual size_t memoryUsageNode() const = 0;
virtual void getMetricMin(double& x, double& y, double& z) = 0;
virtual void getMetricMin(double& x, double& y, double& z) const = 0;
virtual void getMetricMax(double& x, double& y, double& z) = 0;
virtual void getMetricMax(double& x, double& y, double& z) const = 0;
virtual void getMetricSize(double& x, double& y, double& z) = 0;
virtual void prune() = 0;
virtual void expand() = 0;
virtual void clear() = 0;
关于文件读写的方法
- write
- read
- readData 纯虚方法
- writeData 纯虚方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/// Write file header and complete tree to file (serialization)
bool write(const std::string& filename) const;
/**
* Read the file header, create the appropriate class and deserialize.
* This creates a new octree which you need to delete yourself. If you
* expect or requre a specific kind of octree, use dynamic_cast afterwards:
* @code
* AbstractOcTree* tree = AbstractOcTree::read("filename.ot");
* OcTree* octree = dynamic_cast<OcTree*>(tree);
*
* @endcode
*/
static AbstractOcTree* read(const std::string& filename);
/**
* Read all nodes from the input stream (without file header),
* for this the tree needs to be already created.
* For general file IO, you
* should probably use AbstractOcTree::read() instead.
*/
virtual std::istream& readData(std::istream &s) = 0;
/// Write complete state of tree to stream (without file header) unmodified.
/// Pruning the tree first produces smaller files (lossless compression)
virtual std::ostream& writeData(std::ostream &s) const = 0;
- write() 的实现
- 实现了文件头的书写格式,然后调用纯虚函数writeData()写实际数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
bool AbstractOcTree::write(std::ostream &s) const{
s << fileHeader <<"\n# (feel free to add / change comments, but leave the first line as it is!)\n#\n";
s << "id " << getTreeType() << std::endl;
s << "size "<< size() << std::endl;
s << "res " << getResolution() << std::endl;
s << "data" << std::endl;
// write the actual data:
writeData(s);
return true;
}
- read()的实现
- 实现了流的check,文件头部格式的读取校验,创建Tree,然后调用纯虚函数readData()读取具体数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
AbstractOcTree* AbstractOcTree::read(std::istream &s){
// check if first line valid:
std::string line;
std::getline(s, line);
if (line.compare(0,fileHeader.length(), fileHeader) !=0){
OCTOMAP_ERROR_STR("First line of OcTree file header does not start with \""<< fileHeader);
return NULL;
}
std::string id;
unsigned size;
double res;
if (!AbstractOcTree::readHeader(s, id, size, res))
return NULL;
// otherwise: values are valid, stream is now at binary data!
OCTOMAP_DEBUG_STR("Reading octree type "<< id);
AbstractOcTree* tree = createTree(id, res);
if (tree){
if (size > 0)
tree->readData(s);
OCTOMAP_DEBUG_STR("Done ("<< tree->size() << " nodes)");
}
return tree;
}
特别提醒
- createTree的时候会检查classIDMapping的表,对于自定义的tree类型需要用户自行实现注册
- createTree的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
AbstractOcTree* AbstractOcTree::createTree(const std::string class_name, double res){
std::map<std::string, AbstractOcTree*>::iterator it = classIDMapping().find(class_name);
if (it == classIDMapping().end()){
OCTOMAP_ERROR("Could not create octree of type %s, not in store in classIDMapping\n", class_name.c_str());
return NULL;
} else {
AbstractOcTree* tree = it->second->create();
tree->setResolution(res);
return tree;
}
}
此外,用户还需要实现为自定义的类继承create()方法
类型表
- std::map<string, AbstractOcTree*>
- 类型注册函数: registerTreeType()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
private:
/// create private store, Construct on first use
static std::map<std::string, AbstractOcTree*>& classIDMapping();
protected:
static void registerTreeType(AbstractOcTree* tree);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
std::map<std::string, AbstractOcTree*>& AbstractOcTree::classIDMapping(){
// we will "leak" the memory of the map and all trees until program exits,
// but this ensures all static objects are there as long as needed
// http://www.parashift.com/c++-faq-lite/ctors.html#faq-10.15
static std::map<std::string, AbstractOcTree*>* map = new std::map<std::string, AbstractOcTree*>();
return *map;
}
void AbstractOcTree::registerTreeType(AbstractOcTree* tree){
classIDMapping()[tree->getTreeType()] = tree;
}
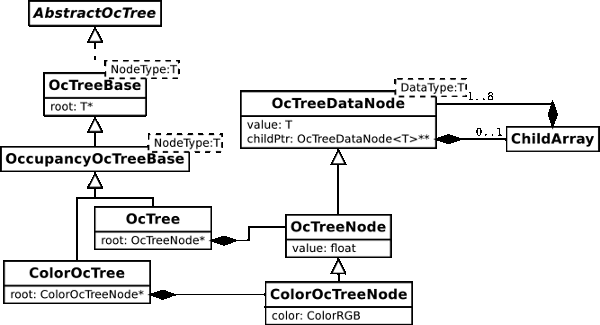
1.1.2 OcTreeBaseImpl
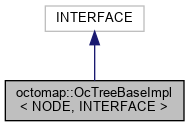
-
INTERFACE 是 AbstractOcTree 或者 AbstractOccupancyOcTree
1 2 3 4
/** * \tparam INTERFACE Interface to be derived from, should be either * AbstractOcTree or AbstractOccupancyOcTree */ -
file
- octomap/include/octomap/OcTreeBaseImpl.h
- octomap/include/octomap/OcTreeBaseImpl.hxx
- 同样是虚基类
1 2
OcTreeBaseImpl(double resolution); virtual ~OcTreeBaseImpl();
- 大小有限制
- 最多16层
- 分辨率最小为0.01
1
2
3
4
/* This tree implementation currently has a maximum depth of 16
* nodes. For this reason, coordinates values have to be, e.g.,
* below +/- 327.68 meters (2^15) at a maximum resolution of 0.01m.
*/
getTreeDepth()
- 获取树的深度
search()
1
2
3
NODE * octomap::OcTreeBaseImpl< NODE, I >::search ( const point3d & value,
unsigned int depth = 0
) const
- Search node at specified depth given a 3d point (depth=0: search full tree depth) You need to check if the returned node is NULL, since it can be in unknown space.
- Returns: pointer to node if found, NULL otherwise.
- 搜索某位置的子节点
getMetricMin()
获取八叉树中所有已分配节点的最小边界坐标。返回的是包含所有有效节点的轴对齐包围盒(AABB)的最小角点坐标,而不是树中数据的最小值。这个函数用于确定八叉树的有效空间范围,通常用于可视化、碰撞检测或空间查询的边界限制。
getMetricMax()
获取最大值
getMetricSize()
= getMetricMax() - getMetricMin()
getRoot()
prune()
expand()
关于文件读写的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// file IO
/**
* Read all nodes from the input stream (without file header),
* for this the tree needs to be already created.
* For general file IO, you
* should probably use AbstractOcTree::read() instead.
*/
std::istream& readData(std::istream &s);
/// Write complete state of tree to stream (without file header) unmodified.
/// Pruning the tree first produces smaller files (lossless compression)
std::ostream& writeData(std::ostream &s) const;
- readData() 和 writeData() 里面分别调用 readNodesRecurs() 和 writeNodesRecurs()
1
2
3
4
5
6
/// recursive call of readData()
std::istream& readNodesRecurs(NODE*, std::istream &s);
/// recursive call of writeData()
std::ostream& writeNodesRecurs(const NODE*, std::ostream &s) const;
- readNodesRecurs() 和 writeNodesRecurs() 的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
template <class NODE,class I>
std::ostream& OcTreeBaseImpl<NODE,I>::writeData(std::ostream &s) const{
if (root)
writeNodesRecurs(root, s);
return s;
}
template <class NODE,class I>
std::ostream& OcTreeBaseImpl<NODE,I>::writeNodesRecurs(const NODE* node, std::ostream &s) const{
node->writeData(s);
// 1 bit for each children; 0: empty, 1: allocated
std::bitset<8> children;
for (unsigned int i=0; i<8; i++) {
if (nodeChildExists(node, i))
children[i] = 1;
else
children[i] = 0;
}
char children_char = (char) children.to_ulong();
s.write((char*)&children_char, sizeof(char));
// std::cout << "wrote: " << value << " "
// << children.to_string<char,std::char_traits<char>,std::allocator<char> >()
// << std::endl;
// recursively write children
for (unsigned int i=0; i<8; i++) {
if (children[i] == 1) {
this->writeNodesRecurs(getNodeChild(node, i), s);
}
}
return s;
}
template <class NODE,class I>
std::istream& OcTreeBaseImpl<NODE,I>::readData(std::istream &s) {
if (!s.good()){
OCTOMAP_WARNING_STR(__FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ << "Warning: Input filestream not \"good\"");
}
this->tree_size = 0;
size_changed = true;
// tree needs to be newly created or cleared externally
if (root) {
OCTOMAP_ERROR_STR("Trying to read into an existing tree.");
return s;
}
root = new NODE();
readNodesRecurs(root, s);
tree_size = calcNumNodes(); // compute number of nodes
return s;
}
template <class NODE,class I>
std::istream& OcTreeBaseImpl<NODE,I>::readNodesRecurs(NODE* node, std::istream &s) {
node->readData(s);
char children_char;
s.read((char*)&children_char, sizeof(char));
std::bitset<8> children ((unsigned long long) children_char);
//std::cout << "read: " << node->getValue() << " "
// << children.to_string<char,std::char_traits<char>,std::allocator<char> >()
// << std::endl;
for (unsigned int i=0; i<8; i++) {
if (children[i] == 1){
NODE* newNode = createNodeChild(node, i);
readNodesRecurs(newNode, s);
}
}
return s;
}
关于光追(Raytracing)的方法
computeRayKeys()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/**
* Traces a ray from origin to end (excluding), returning an
* OcTreeKey of all nodes traversed by the beam. You still need to check
* if a node at that coordinate exists (e.g. with search()).
*
* @param origin start coordinate of ray
* @param end end coordinate of ray
* @param ray KeyRay structure that holds the keys of all nodes traversed by the ray, excluding "end"
* @return Success of operation. Returning false usually means that one of the coordinates is out of the OcTree's range
*/
bool computeRayKeys(const point3d& origin, const point3d& end, KeyRay& ray) const;
- 更推荐使用computeRay(),该函数更快
- 为什么更快,看一看具体实现
computeRay()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
/**
* Traces a ray from origin to end (excluding), returning the
* coordinates of all nodes traversed by the beam. You still need to check
* if a node at that coordinate exists (e.g. with search()).
* @note: use the faster computeRayKeys method if possible.
*
* @param origin start coordinate of ray
* @param end end coordinate of ray
* @param ray KeyRay structure that holds the keys of all nodes traversed by the ray, excluding "end"
* @return Success of operation. Returning false usually means that one of the coordinates is out of the OcTree's range
*/
bool computeRay(const point3d& origin, const point3d& end, std::vector<point3d>& ray);
- 参数:
- origin: ray的起点,世界坐标系下
- end:rat的终点,世界坐标系下
- ray:ray所穿过的grid的中心点
- 算法的实现:
补:KeyRay
-
KeyRay类:光线的表达
-
实现:是一个vector的OcTreeKey
1 2
private: std::vector<OcTreeKey> ray;
1.1.3 OcTreeBase
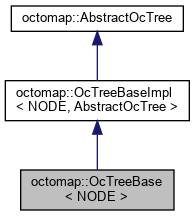
- file
- octomap/include/octomap/OcTreeBase.h
-
实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
template <class NODE> class OcTreeBase : public OcTreeBaseImpl<NODE,AbstractOcTree> { public: OcTreeBase<NODE>(double res) : OcTreeBaseImpl<NODE,AbstractOcTree>(res) {}; /// virtual constructor: creates a new object of same type /// (Covariant return type requires an up-to-date compiler) OcTreeBase<NODE>* create() const {return new OcTreeBase<NODE>(this->resolution); } std::string getTreeType() const {return "OcTreeBase";} };
-
简单包装了一下OcTreeBaseImpl
-
所有的具体方法都在上文的虚类OcTreeBaseImpl里面
-
具体的tree类继承自这个类,用户定义的tree类也可以继承于OcTreeBase, eg:
1 2 3
class MyOcTree : public octomap::OcTreeBase<MyOcTreeNode> { // balabala... };
1.1.4 AbstractOccupancyOcTree
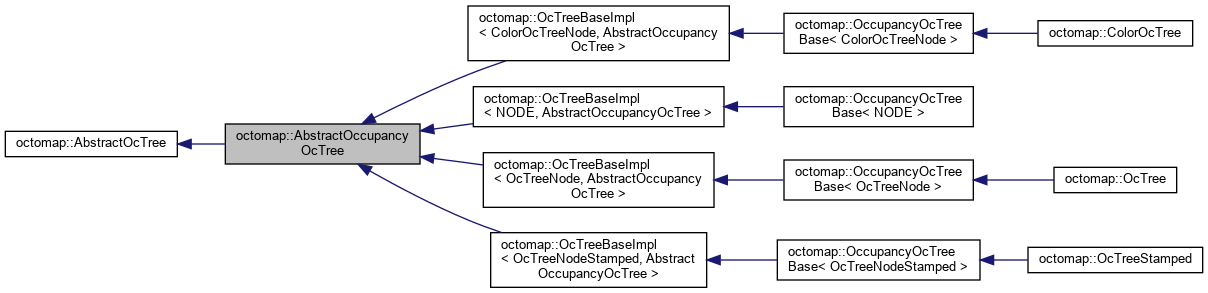
-
file
- octomap/src/AbstractOccupancyOcTree.cpp
- octomap/include/octomap/AbstractOccupancyOcTree.h
-
Interface class for all octree types that store occupancy. 是所有存储占用信息的八叉树的虚基类
-
有许多logodds相关的接口
-
构造函数里面有设置默认的概率更新参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
AbstractOccupancyOcTree::AbstractOccupancyOcTree(){ // some sane default values: setOccupancyThres(0.5); // = 0.0 in logodds setProbHit(0.7); // = 0.85 in logodds setProbMiss(0.4); // = -0.4 in logodds setClampingThresMin(0.1192); // = -2 in log odds setClampingThresMax(0.971); // = 3.5 in log odds }
-
实现了writeBinary() readBinary() 等文件IO方法
文件IO
readBinary()
- 从.bt二进制文件读取octree
writeBinary
- 保存为.bt文件
readBinaryData()
从二进制流中读取八叉树数据的具体实现。该函数负责:
- 读取八叉树的节点数据结构
- 解析二进制格式的占用概率信息
- 重建八叉树的层次结构
- 处理不同版本的二进制格式兼容性
writeBinaryData()
将八叉树数据写入二进制流的具体实现。该函数负责:
- 将节点的占用概率信息序列化为二进制格式
- 保存八叉树的层次结构信息
- 确保数据的紧凑存储和快速读取
- 维护与不同版本的格式兼容性
二进制文件格式说明
OctoMap的二进制文件格式(.bt文件)采用紧凑的存储结构:
- 文件头:包含版本信息、树的分辨率、树的大小等元数据
- 节点数据:采用递归方式存储,每个节点包含:
- 占用概率值(log-odds格式)
- 子节点存在标志位
- 颜色信息(如果是ColorOcTree)
- 压缩优化:相同概率值的节点会被合并,减少存储空间
- 版本兼容:支持向后兼容,可以读取旧版本的文件格式
isNodeOccupied()
1
2
3
4
/// queries whether a node is occupied according to the tree's parameter for "occupancy"
inline bool isNodeOccupied(const OcTreeNode* occupancyNode) const{
return (occupancyNode->getLogOdds() >= this->occ_prob_thres_log);
}
updateNode()
1
2
3
4
5
virtual OcTreeNode* octomap::AbstractOccupancyOcTree::updateNode ( const point3d & value,
bool occupied,
bool lazy_eval = false
)
pure virtual
参数:
| parameters | |
|---|---|
| value | 3d coordinate of the NODE that is to be updated 3d坐标,endpoint |
| occupied | true if the node was measured occupied, else false true表示占据,false表示free |
| lazy_eval | whether update of inner nodes is omitted after the update (default: false). This speeds up the insertion, but you need to call updateInnerOccupancy() when done. |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
template <class NODE>
NODE* OccupancyOcTreeBase<NODE>::updateNode(const point3d& value, bool occupied, bool lazy_eval) {
OcTreeKey key;
if (!this->coordToKeyChecked(value, key))
return NULL;
return updateNode(key, occupied, lazy_eval);
}
概率更新相关参数设置
-
setProbHit()
- sets the probability for a “hit” (will be converted to logodds) - sensor model
-
setProMiss()
- sets the probability for a “miss” (will be converted to logodds) - sensor model
-
setClampingThresMax()
- sets the maximum threshold for occupancy clamping (sensor model)
-
setClampingThresMin()
- sets the minimum threshold for occupancy clamping (sensor model)
-
setOccupancyThres()
- sets the threshold for occupancy (sensor model) 设置occupancy参数
默认参数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
setOccupancyThres(0.5); // = 0.0 in logodds
setProbHit(0.7); // = 0.85 in logodds
setProbMiss(0.4); // = -0.4 in logodds
setClampingThresMin(0.1192); // = -2 in log odds
setClampingThresMax(0.971); // = 3.5 in log odds
具体的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
//-- parameters for occupancy and sensor model:
/// sets the threshold for occupancy (sensor model)
void setOccupancyThres(double prob){occ_prob_thres_log = logodds(prob); }
/// sets the probability for a "hit" (will be converted to logodds) - sensor model
void setProbHit(double prob){prob_hit_log = logodds(prob); assert(prob_hit_log >= 0.0);}
/// sets the probability for a "miss" (will be converted to logodds) - sensor model
void setProbMiss(double prob){prob_miss_log = logodds(prob); assert(prob_miss_log <= 0.0);}
/// sets the minimum threshold for occupancy clamping (sensor model)
void setClampingThresMin(double thresProb){clamping_thres_min = logodds(thresProb); }
/// sets the maximum threshold for occupancy clamping (sensor model)
void setClampingThresMax(double thresProb){clamping_thres_max = logodds(thresProb); }
/// @return threshold (probability) for occupancy - sensor model
double getOccupancyThres() const {return probability(occ_prob_thres_log); }
/// @return threshold (logodds) for occupancy - sensor model
float getOccupancyThresLog() const {return occ_prob_thres_log; }
/// @return probability for a "hit" in the sensor model (probability)
double getProbHit() const {return probability(prob_hit_log); }
/// @return probability for a "hit" in the sensor model (logodds)
float getProbHitLog() const {return prob_hit_log; }
/// @return probability for a "miss" in the sensor model (probability)
double getProbMiss() const {return probability(prob_miss_log); }
/// @return probability for a "miss" in the sensor model (logodds)
float getProbMissLog() const {return prob_miss_log; }
/// @return minimum threshold for occupancy clamping in the sensor model (probability)
double getClampingThresMin() const {return probability(clamping_thres_min); }
/// @return minimum threshold for occupancy clamping in the sensor model (logodds)
float getClampingThresMinLog() const {return clamping_thres_min; }
/// @return maximum threshold for occupancy clamping in the sensor model (probability)
double getClampingThresMax() const {return probability(clamping_thres_max); }
/// @return maximum threshold for occupancy clamping in the sensor model (logodds)
float getClampingThresMaxLog() const {return clamping_thres_max; }
1.1.5 OccupancyOcTreeBase
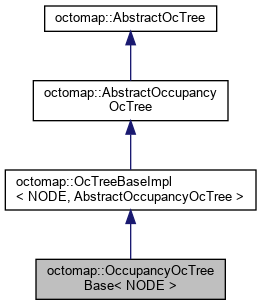
- file
- octomap/include/octomap/OccupancyOcTreeBase.h
- octomap/include/octomap/OccupancyOcTreeBase.hxx
- 比较重要!!!!!
- Base implementation for Occupancy Octrees (e.g. for mapping). 是八叉占据地图的虚基类
- 实现了很多重要函数
insertPointCloud()
-
点云插入函数 Integrate a Pointcloud (in global reference frame), parallelized with OpenMP.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
template<class NODE > void octomap::OccupancyOcTreeBase< NODE >::insertPointCloud ( const Pointcloud & scan, const octomap::point3d & sensor_origin, double maxrange = -1., bool lazy_eval = false, bool discretize = false )
insertPointCloudRays()
setNodeValue()
updateNode()
toMaxLikelihood()
insertRay()
castRay()
1
2
3
4
5
6
virtual bool octomap::OccupancyOcTreeBase< OcTreeNode >::castRay(const point3d & origin,
const point3d & direction,
point3d & end,
bool ignoreUnknownCells = false,
double maxRange = -1.0
) const
-
计算光线
-
参数
- origin: 光束起点,是世界坐标系下sensor(可以是RGBD传感器、也可以是三维激光雷达)的位置
- direction: 光束的方向向量
- 不需要归一化,castRay函数在内部会为我们完成这件事
- end: 返回值,光线击中node的中心位置坐标
-
返回: true if an occupied cell was hit, false if the maximum range or octree bounds are reached, or if an unknown node was hit.
-
函数的参数origin(光束起点)和参数end(传感器末端击中点)都是世界坐标系下的表达!
-
支持并行,可以使用openmp加速
-
getRayIntersection()
-
Retrieves the entry point of a ray into a voxel.
This is the closest intersection point of the ray originating from origin and a plane of the axis aligned cube.
返回光线在体素外壳的进入点的坐标
1
2
3
4
5
6
bool octomap::OccupancyOcTreeBase< NODE >::getRayIntersection ( const point3d & origin,
const point3d & direction,
const point3d & center,
point3d & intersection,
double delta = 0.0
) const
| Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| [in] | origin | Starting point of ray |
| [in] | direction | A vector pointing in the direction of the raycast. Does not need to be normalized. |
| [in] | center | The center of the voxel where the ray terminated. This is the output of castRay. |
| [out] | intersection | The entry point of the ray into the voxel, on the voxel surface. |
| [in] | delta | A small increment to avoid ambiguity of beeing exactly on a voxel surface. A positive value will get the point out of the hit voxel, while a negative valuewill get it inside. |
getNormals()
计算八叉树中占用体素表面的法向量。该函数通过分析相邻体素的占用状态来估算表面法线方向,主要用于:
- 表面重建和网格生成
- 碰撞检测中的接触法线计算
- 路径规划中的表面约束处理
- 可视化渲染中的光照计算
算法通过检查目标体素周围26个邻居体素的占用状态,使用梯度方法估算局部表面的法向量。返回的法向量已归一化,指向自由空间方向。
updateInnerOccupancy()
- 更新八叉树的父节点的数值,避免重复计算
概率更新相关的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
/// integrate a "hit" measurement according to the tree's sensor model
virtual void integrateHit(NODE* occupancyNode) const;
/// integrate a "miss" measurement according to the tree's sensor model
virtual void integrateMiss(NODE* occupancyNode) const;
/// update logodds value of node by adding to the current value.
virtual void updateNodeLogOdds(NODE* occupancyNode, const float& update) const;
/// converts the node to the maximum likelihood value according to the tree's parameter for "occupancy"
virtual void nodeToMaxLikelihood(NODE* occupancyNode) const;
/// converts the node to the maximum likelihood value according to the tree's parameter for "occupancy"
virtual void nodeToMaxLikelihood(NODE& occupancyNode) const;
1.1.6 OcTree
- file
- octomap/src/OcTree.cpp
- octomap/include/octomap/OcTree.h
-
OcTree 作为最顶层的类提供操作所有基本数据结构的方法
- 补充说明
- 在目前的PC机上,github提供的源码实现是通过OpenMP并行计算完成的
- 而Octomap建图还经常使用在无人机上,机载处理器无法像在PC机上实现并行计算,因此ETH ASL实验室的工程人员专门为此开发了适合于无人机应用的Octomap建图程序包volumetric_mapping
- 是OccupancyOcTreeBase的一种具体实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
/**
* octomap main map data structure, stores 3D occupancy grid map in an OcTree.
* Basic functionality is implemented in OcTreeBase.
*
*/
class OcTree : public OccupancyOcTreeBase <OcTreeNode> {
};
-
OcTree里面啥也没有,是简单继承了OccupancyOcTreeBase, 核心代码实现都在 octomap::OccupancyOcTreeBase、octomap::OcTreeBaseImpl两个类里面
-
构造
c++ octomap::OcTree tree(1.0); // create empty tree with resolution 1.0- Node的边界是左闭右开
- tree(1.0) 意味着 [0.0, 1.0) 为一个node, [1.0, 2.0) 为一个node
1.1.7 ColorOcTreeNode
ColorOcTreeNode是OcTreeNode的扩展,在基本占用信息的基础上增加了颜色信息存储功能。
主要特性:
- 继承了OcTreeNode的所有占用概率功能
- 额外存储RGB颜色信息(通常为8位每通道)
- 支持颜色信息的更新和融合
- 用于彩色点云建图和可视化应用
主要方法:
getColor(): 获取节点的RGB颜色值setColor(): 设置节点的RGB颜色值getAverageChildColor(): 计算子节点的平均颜色updateColorChildren(): 更新子节点的颜色信息
1.1.8 CountingOcTree
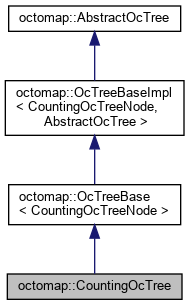
- file
- octomap/src/CountingOcTree.cpp
- octomap/include/octomap/CountingOcTree.h
注:
现在的源码里面是不支持counting_tree的IO,没有实现counting_tree的create() 和 getTreeType()方法
1.2 Node类
1.2.1 AbstractOcTreeNode
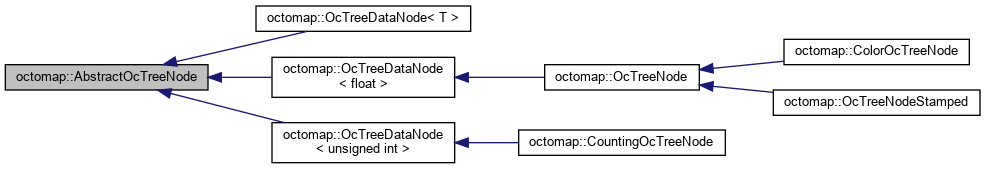
- 所有Node的基类
- file
- octomap/include/octomap/OcTreeDataNode.h
其实是空的:
1
2
3
class AbstractOcTreeNode {
};
1.2.2 OcTreeDataNode
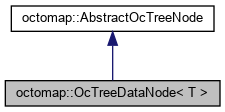
- file
- octomap/include/octomap/OcTreeDataNode.h
- Basic node in the OcTree that can hold arbitrary data of type T in value. This is the base class for nodes used in an OcTree. The used implementation for occupancy mapping is in OcTreeNode.
- \tparam T: data to be stored in the node (e.g. a float for probabilities)
- Note: If you derive a class (directly or indirectly) from OcTreeDataNode, you have to implement (at least) the following functions to avoid slicing errors and memory-related bugs: createChild(), getChild(), getChild() const, expandNode(). See ColorOcTreeNode in ColorOcTree.h for an example.
- 由该类可继承出用户自已的Node类,要求必须至少实现以下接口: createChild(), getChild(), getChild() const, expandNode().
1.2.3 OcTreeNode
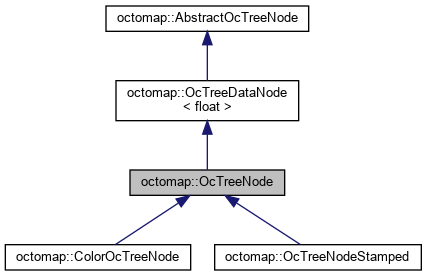
- file
- octomap/include/octomap/OcTreeNode.h
- octomap/src/OcTreeNode.cpp
- Nodes to be used in OcTree. They represent 3d occupancy grid cells. “value” stores their log-odds occupancy.
- OcTreeNode 存储的是log-odd数值,并不是概率值
- Node的边界是左闭右开
getOccupancy()
- 返回occupancy probability
getLogOdds()
- 返回 log odds representation of occupancy probability of node
addValue()
- adds p to the node’s logOdds value (with no boundary / threshold checking!)
1.2.4 ColorOcTreeNode

- file
- octomap/include/octomap/ColorOcTree.h
- octomap/src/ColorOcTree.cpp
1.2.5 CountingOcTreeNode
- file
- octomap/src/CountingOcTree.cpp
- octomap/include/octomap/CountingOcTree.h
- 一个简单的计数tree
- 父节点的value等于子节点的value的合
1.3 OcTreeKey
- is a container class for internal key addressing.
- The keys count the number of cells (voxels) from the origin as discrete address of a voxel.
- 八叉树节点的关键字查询
- 其实就是离散三维点与node元之间的转换
详细接口说明
OcTreeKey是八叉树内部寻址的核心数据结构,提供以下主要接口:
构造函数
OcTreeKey(): 默认构造函数,创建(0,0,0)的keyOcTreeKey(key_type a, key_type b, key_type c): 用三个整数坐标构造keyOcTreeKey(const OcTreeKey& other): 拷贝构造函数
访问操作
key_type& operator[](unsigned int i): 通过索引访问key的分量(i=0,1,2对应x,y,z)const key_type& operator[](unsigned int i) const: 常量版本的索引访问key_type k[3]: 直接访问内部数组
比较操作
bool operator==(const OcTreeKey& other) const: 相等比较bool operator!=(const OcTreeKey& other) const: 不等比较bool operator<(const OcTreeKey& other) const: 小于比较(用于排序)
实用方法
std::string toString() const: 转换为字符串表示size_t computeHash() const: 计算哈希值,用于哈希表存储
OcTreeKey的主要作用是将连续的三维坐标空间离散化为整数网格坐标,便于八叉树的快速索引和查找操作。
1.4 OctoTreeParam
参数类,用于管理八叉树的各种配置参数。
主要参数类型
基本参数
resolution: 八叉树的分辨率(米)max_depth: 最大树深度tree_type: 树的类型标识符
概率更新参数
prob_hit: 传感器击中的概率prob_miss: 传感器未击中的概率prob_thres_min: 最小概率阈值prob_thres_max: 最大概率阈值occupancy_thres: 占用判定阈值
文件IO参数
file_format_version: 文件格式版本compression_level: 压缩级别binary_format: 是否使用二进制格式
该类提供统一的参数管理接口,支持参数的序列化、反序列化和验证功能。
1.5 iterator
迭代器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
octomap::OcTree* tree = new octomap::OcTree(1.0);
unsigned int maxDepth = tree->getTreeDepth();
std::vector<octomap::OcTreeNode*> collapsed_occ_nodes;
for (octomap::OcTree::iterator it = tree->begin(); it != tree->end(); ++it) {
if (tree->isNodeOccupied(*it) && it.getDepth() < maxDepth) {
collapsed_occ_nodes.push_back(&(*it));
}
}
getDepth()
- 返回深度
getCoordinate()
- return the center coordinate of the current node 返回node的中心位置坐标
1.6 ScanGraph
- A ScanGraph is a collection of ScanNodes, connected by ScanEdges. Each ScanNode contains a 3D scan performed from a pose.
readPlainASCII()
-
读取 InputFile.log
-
文件格式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
std::cerr << "The log file needs to be in the format of:\n"
<< "NODE x y z roll pitch yaw\n"
<< "x y z\nx y z\n...\n"
<< "NODE x y z roll pitch yaw\n"
<< "x y z\n...\n\n"
<< "Lines starting with '#' or empty lines are ignored.\n\n";
writeBinary()
- 写入 OutputFile.graph
1.7 ScanNode
ScanNode表示扫描图中的一个节点,包含从特定位姿获取的3D扫描数据。
主要组成部分
位姿信息
pose: 扫描时传感器的6DOF位姿(位置+姿态)scan_time: 扫描的时间戳node_id: 节点的唯一标识符
扫描数据
scan: 包含的点云数据(Pointcloud对象)scan_size: 扫描点的数量max_range: 扫描的最大有效距离
主要方法
getScan(): 获取点云数据getPose(): 获取位姿信息getMaxRange(): 获取最大扫描距离writeBinary()/readBinary(): 二进制序列化接口
ScanNode通常用于SLAM系统中存储历史扫描数据,支持回环检测和地图优化。
1.8 ScanEdge
ScanEdge表示扫描图中两个ScanNode之间的连接关系,通常表示相对位姿变换。
主要组成部分
连接信息
first_node_id: 起始节点IDsecond_node_id: 目标节点IDtransform: 两节点间的相对变换矩阵weight: 边的权重(表示置信度)
约束类型
constraint_type: 约束类型(里程计、回环等)information_matrix: 信息矩阵(协方差的逆)edge_id: 边的唯一标识符
主要方法
getTransform(): 获取相对变换getWeight(): 获取边权重getInformationMatrix(): 获取信息矩阵writeBinary()/readBinary(): 序列化接口
ScanEdge用于构建位姿图,支持图优化算法进行全局一致性优化,是SLAM后端优化的重要数据结构。
1.9 文件格式
example: http://docs.ros.org/en/melodic/api/octomap/html/convert__octree_8cpp_source.html
.bt
the occupied voxels of a binary OctoMap file.
.bt.wrl
VRML2.0 file.
.ot
OctoMap octree file formats. 最新的文件格式
.graph
scan graph file (point clouds with poses).
.log
a plain text log file.
Examples and Tests
- examples http://octomap.github.io/octomap/doc/files.html
- unit-tests http://octomap.github.io/octomap/doc/dir_3513c77e68d0de165c8b48f945306dcb.html
Contact
Feel free to contact me windmillyucong@163.com anytime for anything.