DEMO
Created 2021.06.11 by Cong Yu; Last modified: 2021.06.11-v1.0.2
Contact: windmillyucong@163.com
Copyleft! 2022 Cong Yu. Some rights reserved.
todo(congyu)
IMU 积分总结
IMU 动力学公式
时间导数

公式中的 wbt 表示 t时刻w系下b的位姿
连续时间的积分公式

离散时间的积分公式
1. 欧拉法
k+1的结果是由k时刻的测量值计算出来的
公式: (vio_learning, l2, p40)
以及 pdf(Course on SLAM, p11)
2. 中值法
公式: (vio_learning, l2, p41)
以及 pdf(Course on SLAM, p11)
3. 龙格库塔
todo(congyu)
注意上述公式中的姿态积分都是用的四元数的形式表达出来的,也有很多其他积分表达方式
Gyro积分的几种表达方式总结
公式: (vio_learning, l2, p43)
1. 四元数形式的积分:
\[q_{wb} \leftarrow q_{wb} \otimes \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ \frac 1 2 \mathbf {\omega\Delta t}\end{bmatrix}\]- $q_{wb}$ 表示 w坐标系下 b 系的姿态。
- $\omega$ 表示IMU在b系下的测量值即可。
2. SO3形式(旋转矩阵)的积分:
\[R{wb} \leftarrow R_{wb} \text{exp}(\mathbf {\omega\Delta t})\]3. 欧拉角形式的积分:
\(\chi_{wb} \leftarrow \chi_{wb} + E_{wb} \mathbf {\omega\Delta t}\) 其中:
$\chi = (Y_{aw}, P_{itch}, R_{oll})^T$ 表示欧拉角
$E_{wb}$ 表示将IMU 坐标系下得到的角速度测量值投影到欧拉角速度
$E_{wb}$ 的推导:
特别注意:IMU 测量值需要做投影!!!
投影公式推导:
- 公式: (vio_learning, l2, p44-46)
- 投影步骤
预积分
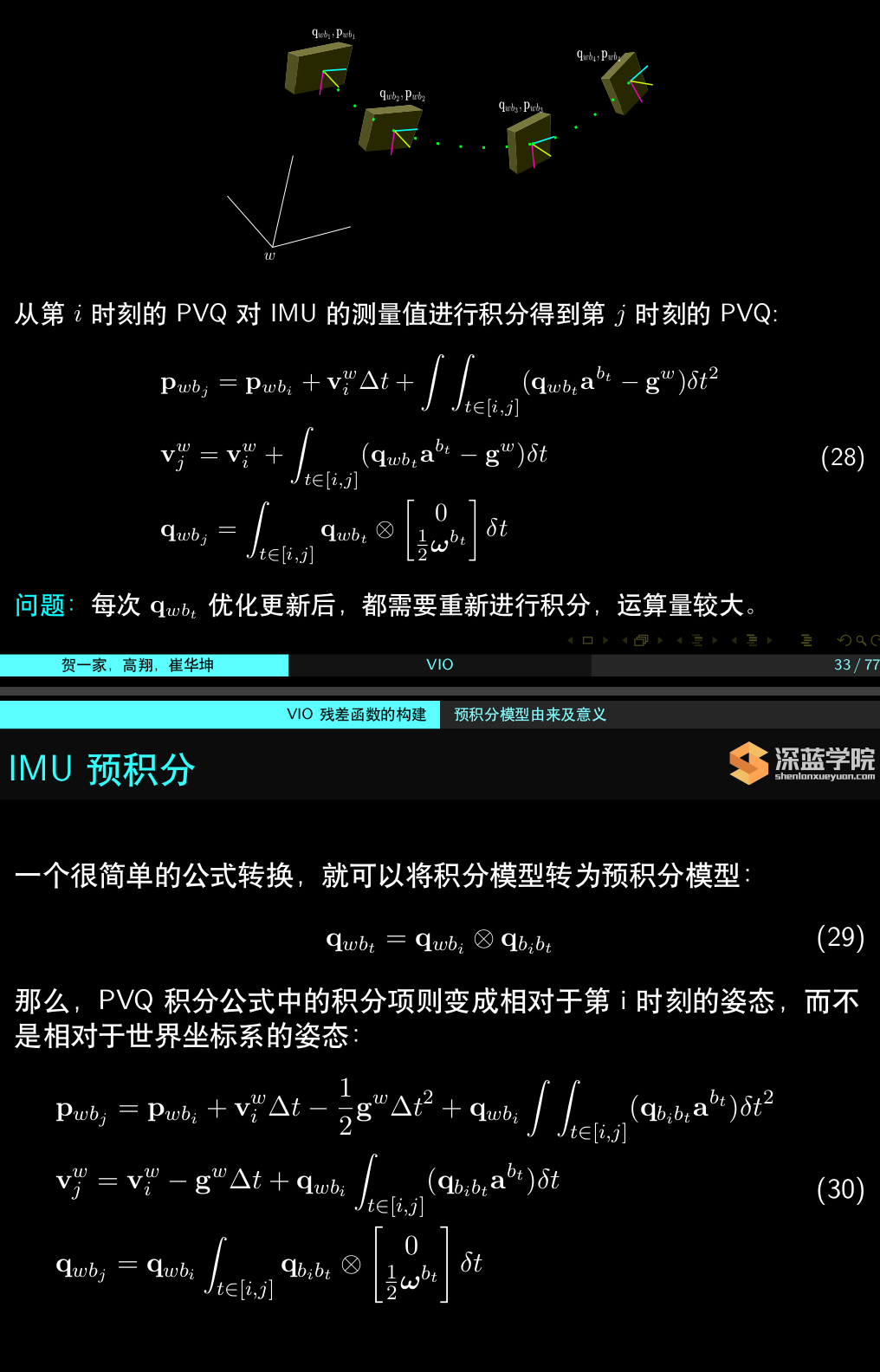 注意一个问题:
注意一个问题:
- VIO中直接对陀螺仪积分求姿态,直接对加速度积分求位置
- 并不像 Mahony算法中,使用加速度计对陀螺仪做补偿
- mahony 算法中假定加速度计测量的只有重力加速度,这是怎么回事?
Inertial measurement units (IMU) and the related motion model are useful for agile plat- forms with or without contact to the ground. IMU measurements of acceleration a S and angular rates ω S are taken as control signals in the sense that they are used to predict the future pose of the robot.
\[{\small X} = \begin{bmatrix} p \\ v \\ q \\a_b \\\omega_b \end{bmatrix}, u= \begin{bmatrix} a_S \\ \omega_S \end{bmatrix}, i = \begin{bmatrix} {\small{V_i}} \\ \theta_i \\ a_i \\ \omega_i \end{bmatrix}\] \[\begin{align} p &← p + v \Delta t + (R\{q\}(a_S − a_b ) + g) \Delta t^2 \\ v &← v + (R\{q\}(a_S − a_b ) + g) \Delta t + {\small{V}}_i \\ q &← q ⊗ q\{(\omega_S -\omega_b)\Delta t+\theta_i\} \\ a_b &← a_b + a_i \\ \omega_b &← \omega_b + \omega_i \end{align}\]where p, v, q are respectively the position, velocity and orientation quaternion of the IMU reference frame, a b and ω b are respectively the accelerometer and gyrometer biases, v i and θ i are perturbation impulses due to the measurement noises integrated over the time step ∆t, and a i and w i are the biases’ random walks.